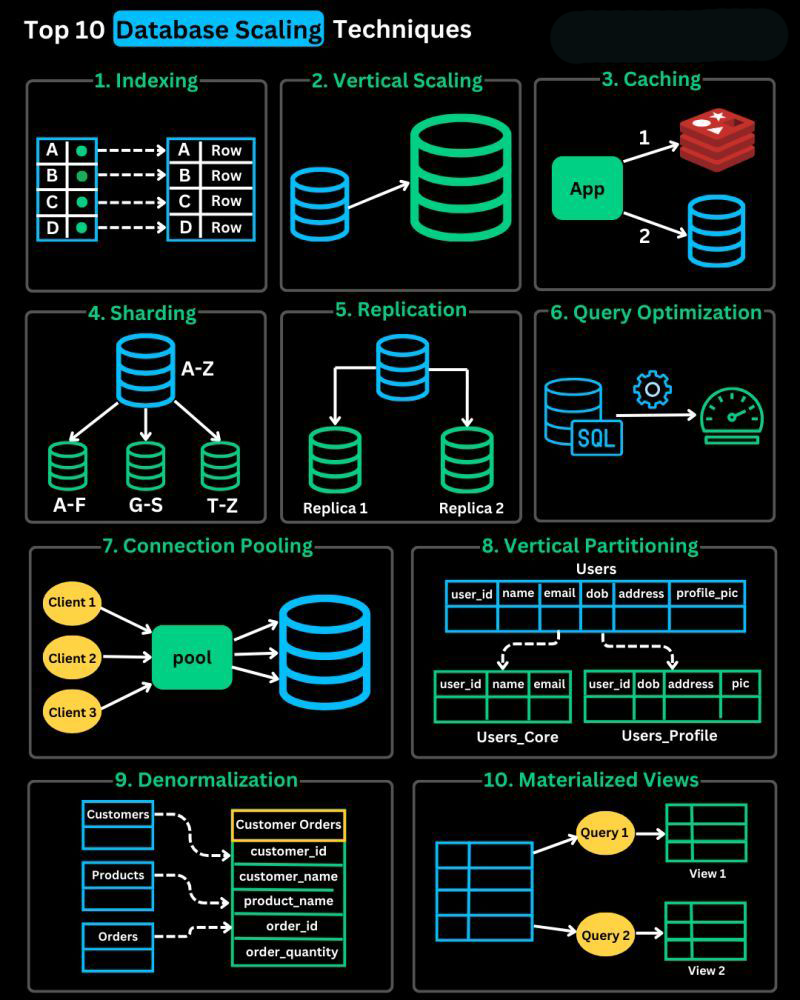
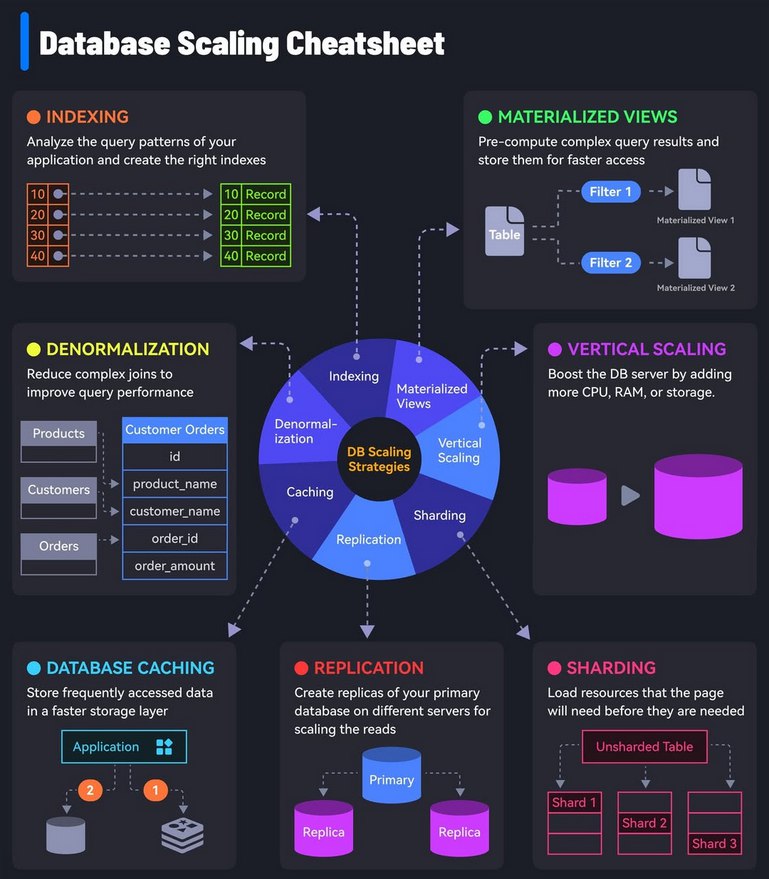
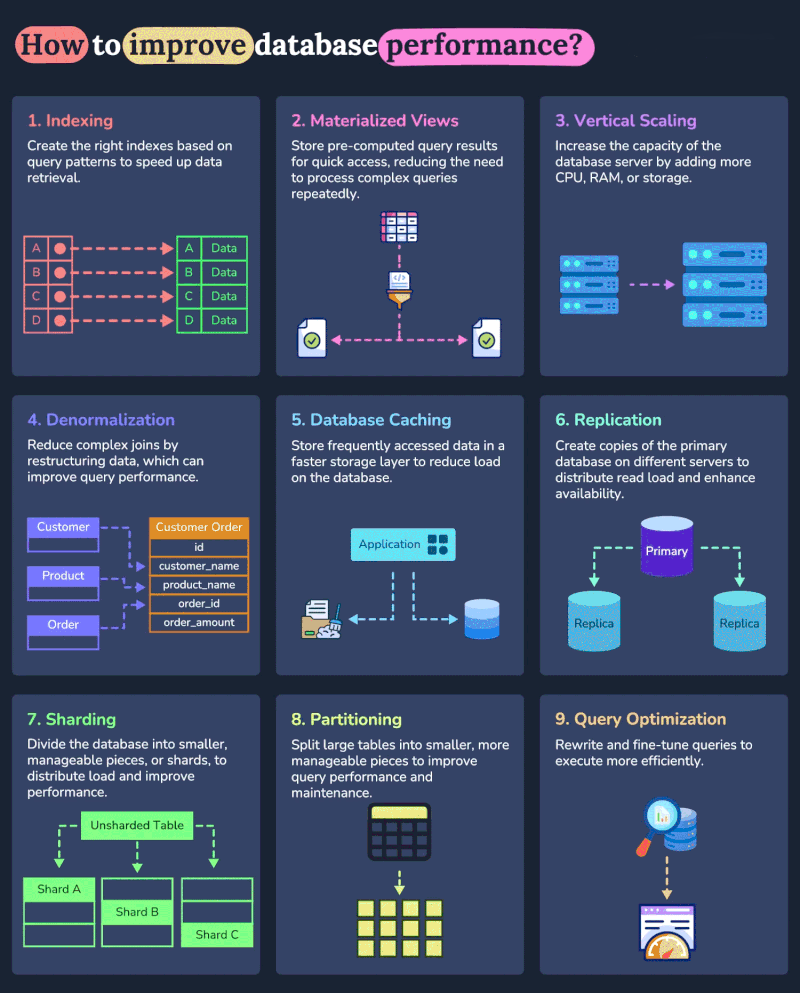
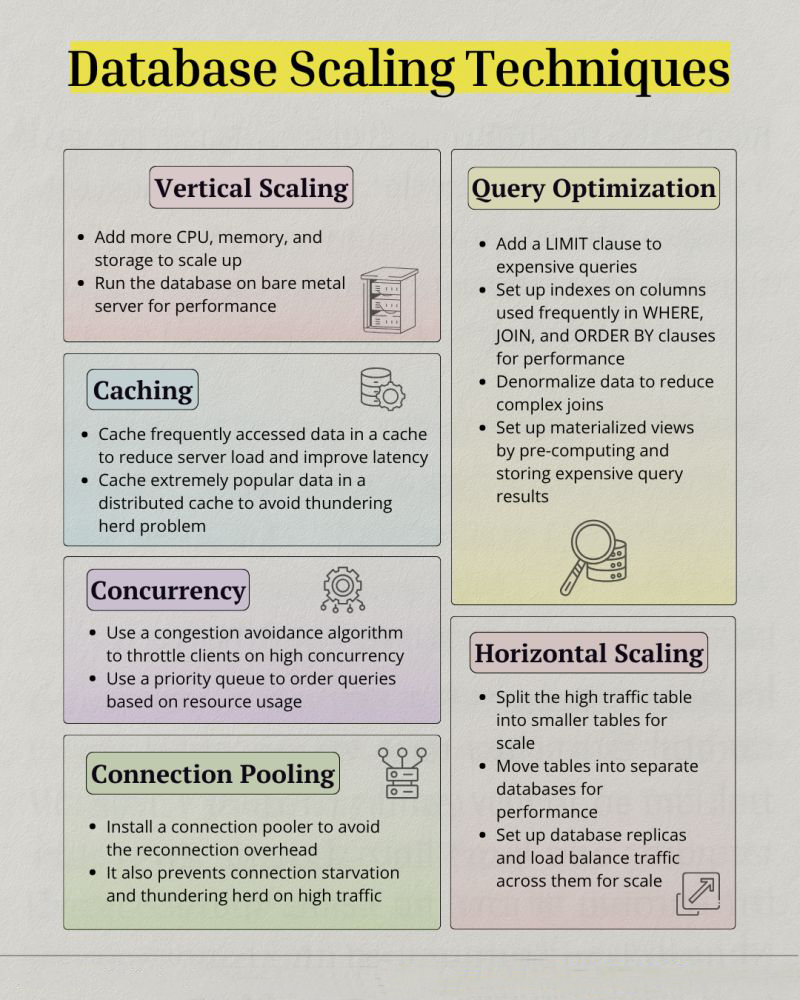
Scaling¶
Overview¶
Sequences¶
1. Query Optimization (First Priority)¶
-- Before optimization
SELECT * FROM users WHERE age > 25;
-- After optimization
SELECT id, name FROM users
WHERE age > 25
LIMIT 100;
2. Database Indexing¶
-- Add indexes for frequently queried columns
CREATE INDEX idx_user_age ON users(age);
CREATE INDEX idx_user_email ON users(email);
-- Composite index for multiple columns
CREATE INDEX idx_user_age_city ON users(age, city);
3. Caching Implementation¶
# Example using Redis cache
def get_user(user_id):
# Try cache first
cached_user = redis_cache.get(f"user:{user_id}")
if cached_user:
return cached_user
# If not in cache, get from DB and cache it
user = database.query(f"SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = {user_id}")
redis_cache.set(f"user:{user_id}", user, expire=3600)
return user
4. Vertical Scaling (Scale Up)¶
- Increase CPU
- Add more RAM
- Upgrade to faster storage (SSD/NVMe)
5. Database Partitioning¶
-- Example of date-based partitioning
CREATE TABLE orders (
order_id INT,
order_date DATE,
amount DECIMAL
) PARTITION BY RANGE (YEAR(order_date)) (
PARTITION p2022 VALUES LESS THAN (2023),
PARTITION p2023 VALUES LESS THAN (2024),
PARTITION p2024 VALUES LESS THAN (2025)
);
6. Read Replicas¶
7. Horizontal Scaling (Sharding)¶
8. Database Type Optimization¶
Right choice DB based on demand
Transactions → PostgreSQL/MySQL
Analytics → ClickHouse/Redshift
Caching → Redis
Document Storage → MongoDB
Graph Data → Neo4j
9. Microservices Split¶
10. Geographic Distribution¶
US Region:
- Primary DB
- Read Replicas
EU Region:
- Primary DB
- Read Replicas
Asia Region:
- Primary DB
- Read Replicas
Partitioning¶
1.Types of Partitioning¶
A. Range Partitioning¶
-- Partition by date range
CREATE TABLE sales (
id INT,
sale_date DATE,
amount DECIMAL
) PARTITION BY RANGE (YEAR(sale_date)) (
PARTITION p_2022 VALUES LESS THAN (2023),
PARTITION p_2023 VALUES LESS THAN (2024),
PARTITION p_2024 VALUES LESS THAN (2025),
PARTITION p_future VALUES LESS THAN MAXVALUE
);
-- Partition by amount range
CREATE TABLE orders (
order_id INT,
amount DECIMAL
) PARTITION BY RANGE (amount) (
PARTITION p_small VALUES LESS THAN (100),
PARTITION p_medium VALUES LESS THAN (1000),
PARTITION p_large VALUES LESS THAN (10000),
PARTITION p_huge VALUES LESS THAN MAXVALUE
);
ASCII Visualize
ALL SALES DATA
┌───────────────────┐
│ Database │
└─────────┬─────────┘
│
┌─────┴─────┬────────────┬────────────┐
│ │ │ │
┌───▼───┐ ┌───▼───┐ ┌───▼───┐ ┌───▼───┐
│ 2022 │ │ 2023 │ │ 2024 │ │Future │
│ Sales │ │ Sales │ │ Sales │ │ Sales │
└───────┘ └───────┘ └───────┘ └───────┘
B. List Partitioning¶
-- Partition by region
CREATE TABLE customers (
id INT,
name VARCHAR(100),
country VARCHAR(50)
) PARTITION BY LIST (country) (
PARTITION p_europe VALUES IN ('France', 'Germany', 'Spain'),
PARTITION p_asia VALUES IN ('China', 'Japan', 'India'),
PARTITION p_americas VALUES IN ('USA', 'Canada', 'Brazil')
);
ASCII Visualize
CUSTOMER DATA
┌──────────────────┐
│ Database │
└────────┬─────────┘
│
┌─────────┼─────────┐
│ │ │
┌───▼───┐ ┌───▼───┐ ┌───▼───┐
│EUROPE │ │ ASIA │ │ USA │
│France │ │ China │ │ Texas │
│Spain │ │ Japan │ │ NYC │
│Italy │ │ India │ │ LA │
└───────┘ └───────┘ └───────┘
C. Hash Partitioning¶
-- Automatically distribute data across 4 partitions
CREATE TABLE users (
id INT,
email VARCHAR(100)
) PARTITION BY HASH(id) PARTITIONS 4;
ASCII Visualize
USER DATA (Hash by ID)
┌─────────────────────────┐
│ Database │
└────────────┬────────────┘
│
┌───────┴──────┐
│ Hash(ID) │
└───────┬──────┘
┌─────────┼─────────┐
│ │ │
┌──▼───┐ ┌──▼───┐ ┌──▼───┐
│ P0 │ │ P1 │ │ P2 │
│ID%3=0│ │ID%3=1│ │ID%3=2│
└──────┘ └──────┘ └──────┘
2. Composite Partitioning (Combining Multiple Types)¶
-- Partition by year and then by month
CREATE TABLE transactions (
id INT,
trans_date DATE,
amount DECIMAL
) PARTITION BY RANGE (YEAR(trans_date))
SUBPARTITION BY HASH(MONTH(trans_date))
SUBPARTITIONS 12 (
PARTITION p_2023 VALUES LESS THAN (2024),
PARTITION p_2024 VALUES LESS THAN (2025)
);
ASCII Visualize
SALES DATABASE
┌──────────────────────────┐
│ 2023 │
└───────────┬──────────────┘
│
┌───────────────┼───────────────┐
│ │ │
┌───▼───┐ ┌───▼───┐ ┌───▼───┐
│ Q1 │ │ Q2 │ │ Q3 │
└──┬────┘ └──┬────┘ └──┬────┘
│ │ │
├─Jan ├─Apr ├─Jul
├─Feb ├─May ├─Aug
└─Mar └─Jun └─Sep
3. Partition Management¶
A. Adding New Partitions¶
-- Add new partition for next year
ALTER TABLE sales ADD PARTITION (
PARTITION p_2025 VALUES LESS THAN (2026)
);
B. Removing Partitions¶
C. Reorganizing Partitions¶
4. Querying Partitioned Tables¶
A. Partition Pruning (Automatic)¶
-- Database will only scan relevant partitions
SELECT * FROM sales
WHERE sale_date BETWEEN '2023-01-01' AND '2023-12-31';
B. Partition Selection¶
5. Best Practices¶
A. Sizing Guidelines¶
-- Keep partitions similarly sized
CREATE TABLE logs (
id INT,
log_date DATE,
message TEXT
) PARTITION BY RANGE (UNIX_TIMESTAMP(log_date)) (
PARTITION p1 VALUES LESS THAN (UNIX_TIMESTAMP('2023-04-01')),
PARTITION p2 VALUES LESS THAN (UNIX_TIMESTAMP('2023-07-01')),
PARTITION p3 VALUES LESS THAN (UNIX_TIMESTAMP('2023-10-01'))
);
6. Common Use Cases¶
A. Time-Based Data Management¶
-- Archiving old data
CREATE TABLE archive_sales
SELECT * FROM sales PARTITION (p_2022);
ALTER TABLE sales DROP PARTITION p_2022;
B. Geographic Data Distribution¶
-- Regional data access
CREATE TABLE user_data (
id INT,
region VARCHAR(50),
data TEXT
) PARTITION BY LIST (region) (
PARTITION p_us VALUES IN ('us-east', 'us-west'),
PARTITION p_eu VALUES IN ('eu-central', 'eu-west'),
PARTITION p_asia VALUES IN ('asia-east', 'asia-south')
);
ASCII Visualize
Before Partitioning After Partitioning
┌──────────────────┐ ┌─────────┐ ┌─────────┐
│ ░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░ │ │ ░░░░░░░ │ │ ░░░░░░░ │
│ ░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░ │ │ ░░░░░░░ │ │ ░░░░░░░ │
│ ░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░ │ => │ ░░░░░░░ │ │ ░░░░░░░ │
│ ░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░ │ └─────────┘ └─────────┘
└──────────────────┘ ┌─────────┐ ┌─────────┐
│ ░░░░░░░ │ │ ░░░░░░░ │
Single Table │ ░░░░░░░ │ │ ░░░░░░░ │
└─────────┘ └─────────┘
Partitioned Tables
7. Monitoring Partitions¶
-- View partition information
SELECT
PARTITION_NAME,
TABLE_ROWS,
DATA_LENGTH,
INDEX_LENGTH
FROM
INFORMATION_SCHEMA.PARTITIONS
WHERE
TABLE_NAME = 'sales';
Query Flow in Partitioned Table:
Query: SELECT * FROM sales WHERE date = '2023-06-15'
┌─────────────┐
│ Query │
└─────┬───────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────┐ ┌───────────┐
│ Partition │───→│ 2022 Data │ (Skip)
│ Manager │ └───────────┘
└─────┬───────┘ ┌───────────┐
│───────────→│ 2023 Data │ (Search)
│ └───────────┘
│ ┌───────────┐
└───────────→│ 2024 Data │ (Skip)
└───────────┘
Key Benefits¶
- Improved query performance
- Easier maintenance
- Better data lifecycle management
- Improved backup/recovery options
- Parallel query execution potential
Common Pitfalls to Avoid¶
- Over-partitioning
- Wrong partition key selection
- Not planning for growth
- Ignoring maintenance overhead
- Not considering query patterns
Horizontal Scaling (Scaling Out)¶
Definitions¶
- The process of adding more machines to your existing system to handle increased load and distribute it across multiple servers
- Instead of upgrading existing hardware (vertical scaling / scale up), you add more instances of servers
- Distributes load across multiple servers while keeping data synchronized
Key Components¶
A. Load Balancer¶
- A device/software that distributes incoming network traffic across multiple servers
- Ensures no single server bears too much load
- Provides failover if one server goes down
B. Replication (Read Path)¶
- Process of copying data from one database server (master) to others (replicas)
- Improves read performance and provides redundancy
- Helps distribute database load across multiple servers
C. Sharding (Write Path)¶
- Technique of splitting database into smaller parts (shards)
- Each shard contains unique portions of data
- Improves write performance and handles large datasets
Examples¶
Social Media Platform¶
Before Scaling:
Single Server
- 1 million users
- Slow photo uploads
- Delayed notifications
- Frequent crashes
After Horizontal Scaling:
└── Load Balancer
├── Server 1: User Authentication
├── Server 2: Photo Processing
├── Server 3: Notification System
└── Database Layer
├── Shard 1: Users A-M
└── Shard 2: Users N-Z
E-commerce Website¶
Before: Single server handling:
- Product catalog
- User accounts
- Orders
- Payment processing
After Horizontal Scaling:
└── Load Balancer
├── Web Servers (3 instances)
│ └── Product Browsing
├── Application Servers
│ ├── Server 1: User Management
│ ├── Server 2: Order Processing
│ └── Server 3: Payment Handling
└── Database Layer
├── Products DB (Master + 2 replicas)
├── Orders DB (Sharded by date)
└── Users DB (Sharded by region)
Video Streaming Service¶
Original Setup:
- Single server
- Limited concurrent streams
- Buffering issues
- Regional delays
Horizontally Scaled:
└── Global Load Balancer
├── US Region
│ ├── Content Servers (5)
│ └── User Database Shard
├── EU Region
│ ├── Content Servers (4)
│ └── User Database Shard
└── Asia Region
├── Content Servers (6)
└── User Database Shard
Banking Application¶
Traditional Setup:
- Single core banking server
- Limited transaction processing
- Slow during peak hours
Scaled Architecture:
└── Load Balancer
├── Transaction Servers
│ ├── Server 1: Deposits
│ ├── Server 2: Withdrawals
│ └── Server 3: Transfers
└── Database Layer
├── Account DB
│ ├── Shard 1 (A-M)
│ └── Shard 2 (N-Z)
└── Transaction DB
├── Current Month (Master)
└── Historical (Replicas)