Linker & Loader¶
we have to understand some concept that related to this topic.
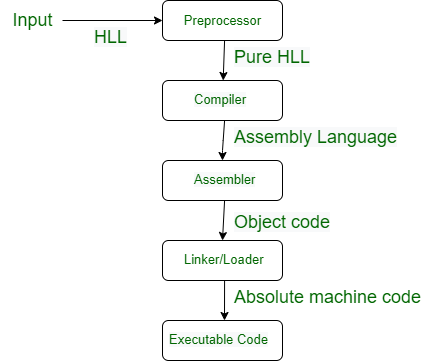
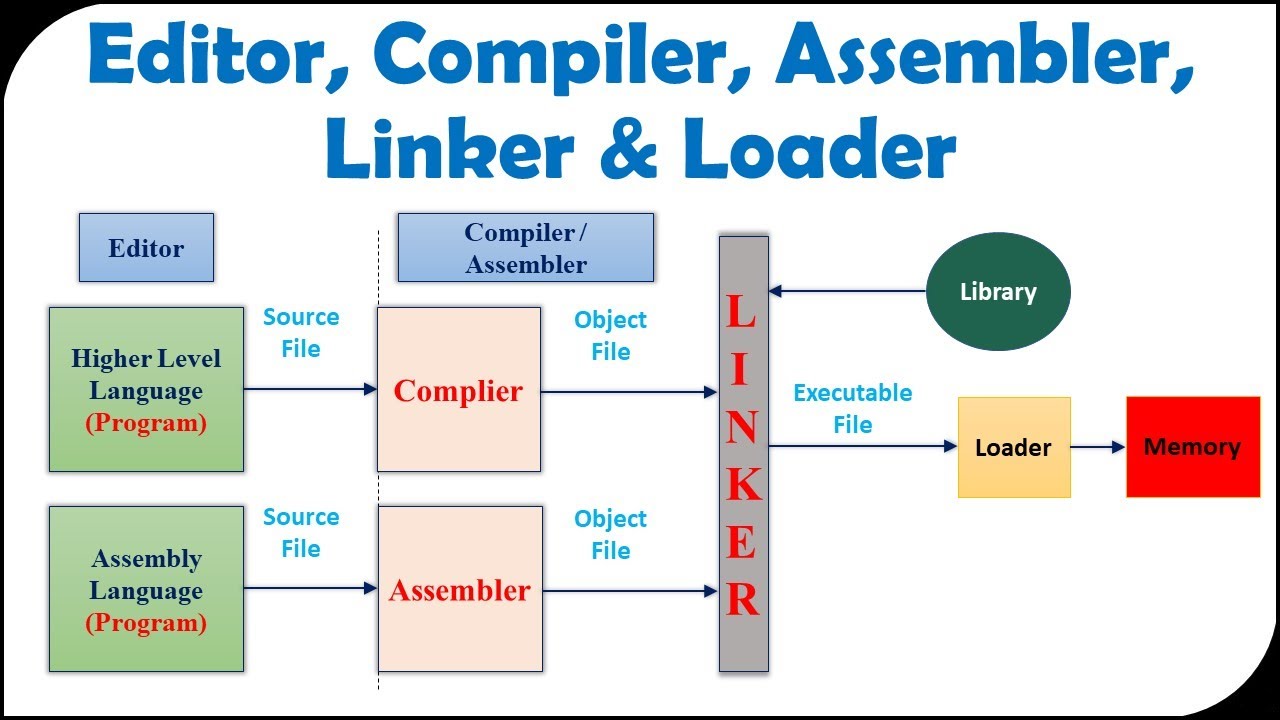
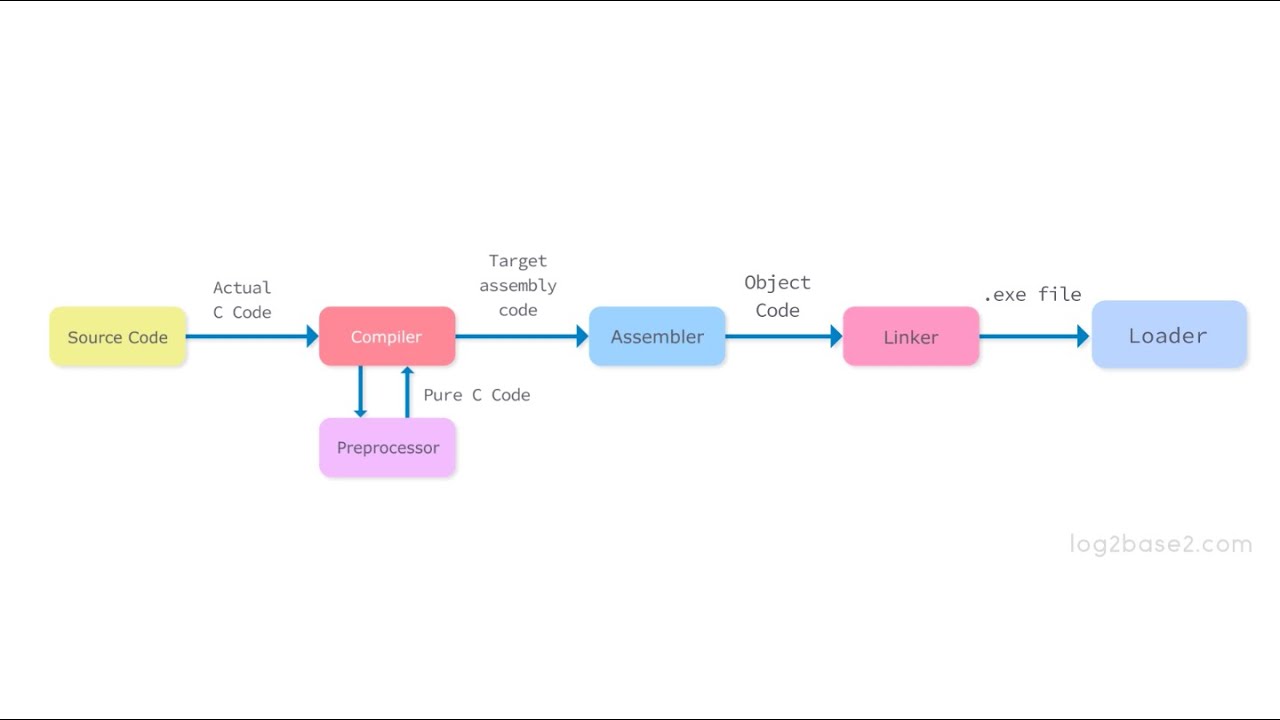
Preprocessor¶
- It includes all header files and also evaluates whether a macro(A macro is a piece of code that is given a name. Whenever the name is used, it is replaced by the contents of the macro by an interpreter or compiler. The purpose of macros is either to automate the frequency used for sequences or to enable more powerful abstraction) is included. It takes source code as input and produces modified source code as output. The preprocessor is also known as a macro evaluator, the processing is optional that is if any language that does not support
#includemacros processing is not required.
Compiler¶
- The compiler takes the modified code as input and produces the target code as output.
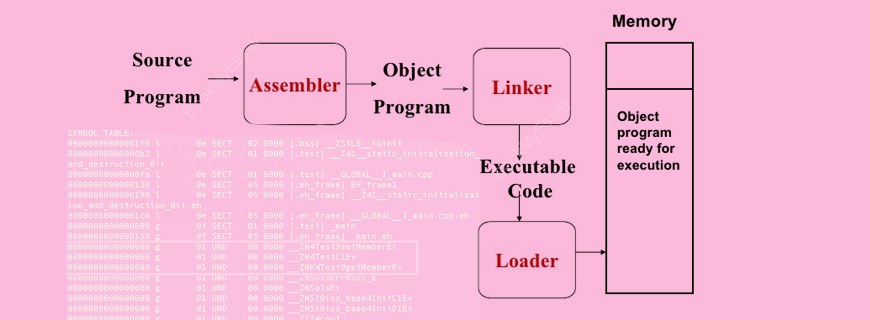
Assembler¶
- The assembler takes the target code as input and produces real locatable machine code as output.
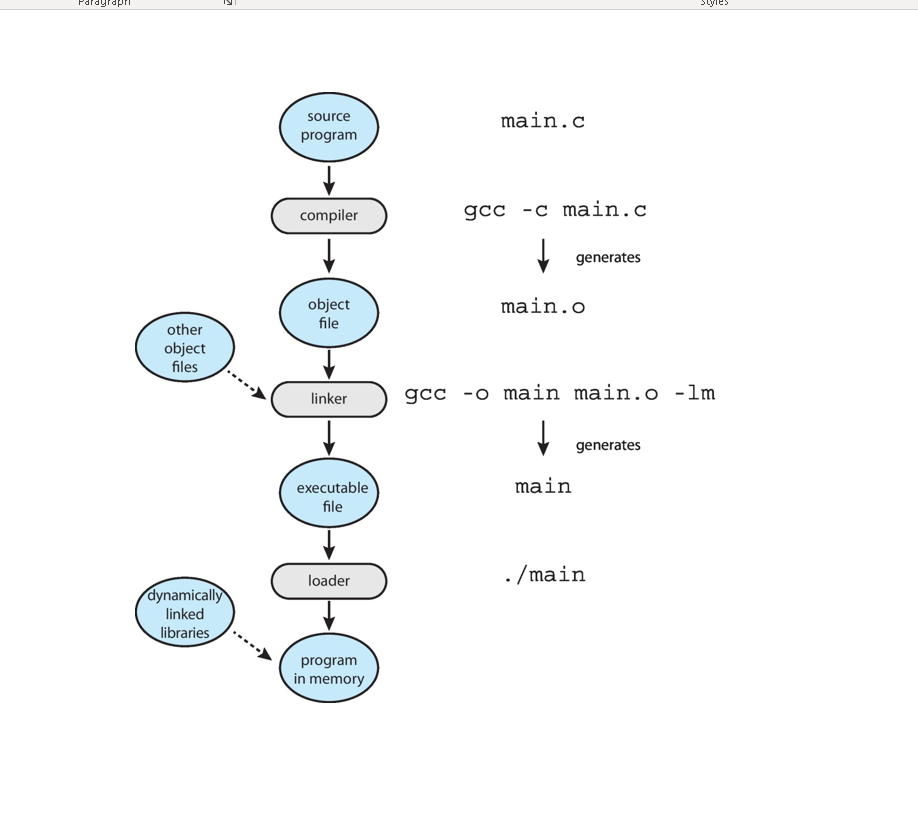
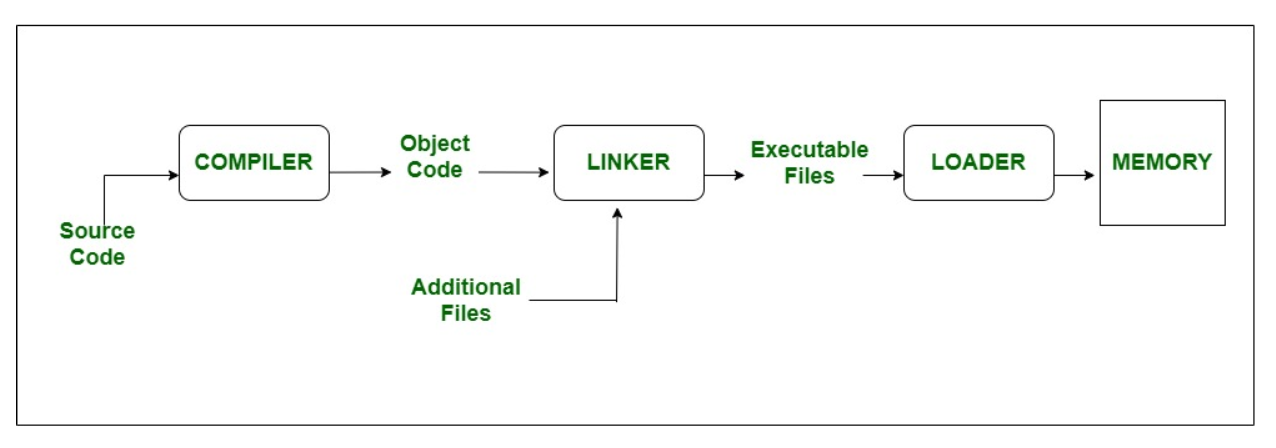
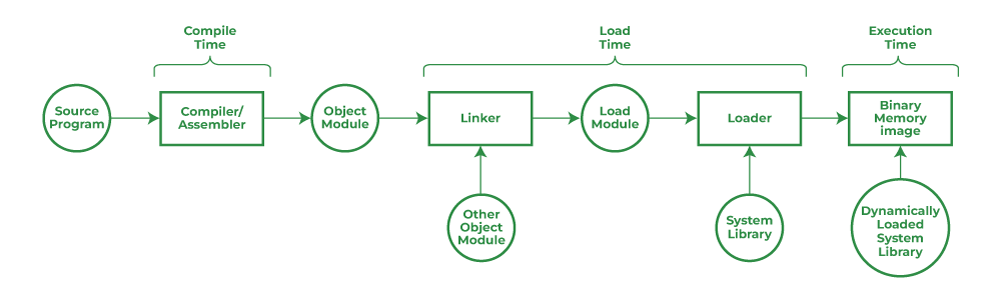
Linker¶
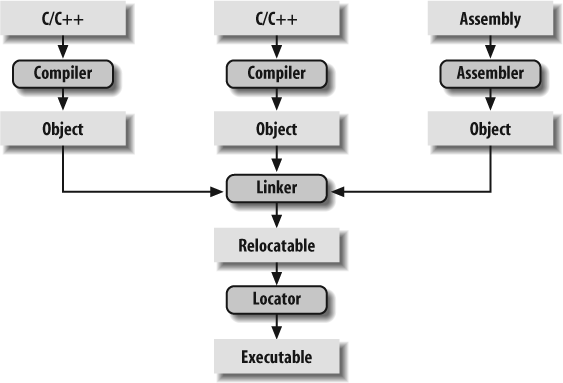
- Linker or link editor is a program that takes a collection of objects (created by assemblers and compilers) and combines them into an executable program.
Loader¶
- The loader keeps the linked program in the main memory.
Executable code¶
- It is low-level and machine-specific code that the machine can easily understand. Once the job of the linker and loader is done the object code is finally converted it into executable code.
There are some schemas for better understanding¶
Functions of loader¶
Allocation¶
- It is used to allocate space for memory in an object program. A translator cannot allocate space because there may be overlap or large waste of memory.
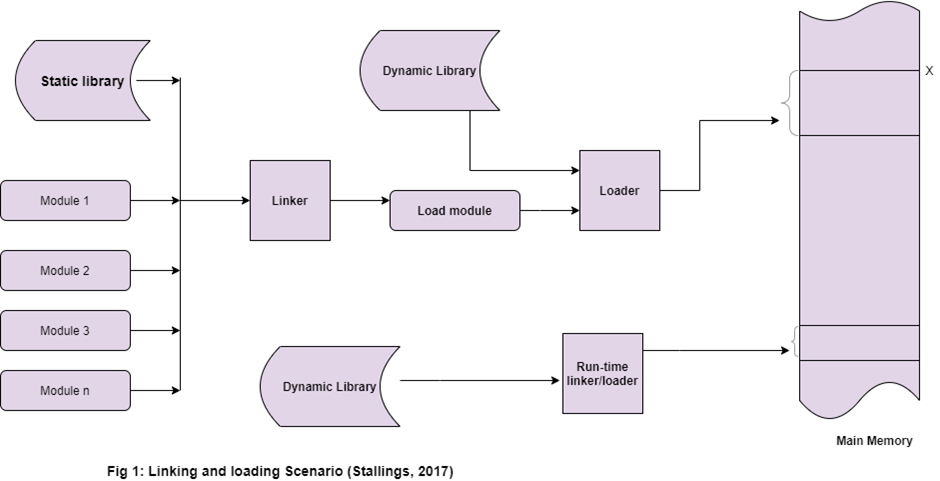
Linking¶
- It combines two or more different object programs and resolves the symbolic context between object decks. It also provides the necessary information to allow reference between them. Linking is of two types as follows.
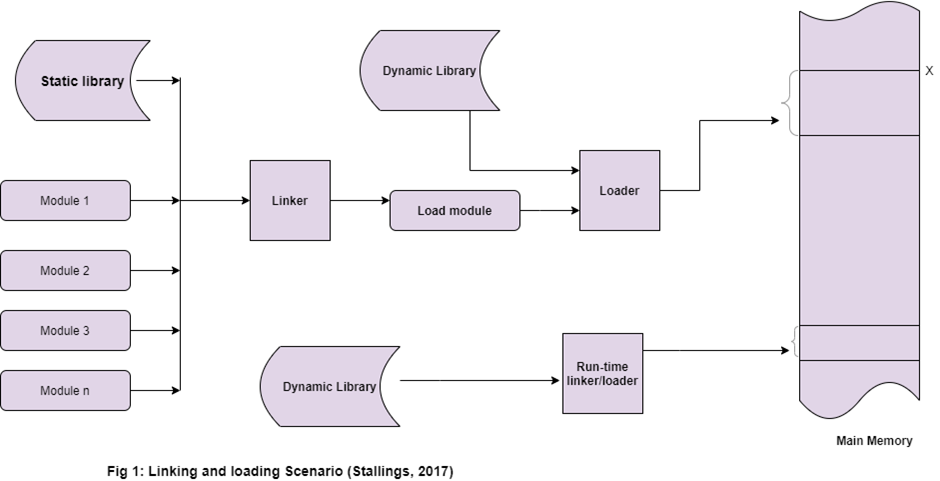
Static Linking¶
- It copies all the library routines used in the program into an executable image. This requires more disk space and memory.
Dynamic Linking¶
- It resolves undefined symbols while a program is running. This means that executable code still has undefined symbols and a list of objects or libraries that will provide definitions for the same.
Reallocation¶
- This object modifies the program so that it can be loaded to an address different from the originally specified location, and to accommodate all addresses between dependent locations.
Loading¶
- Physically, it keeps machine instructions and data in memory for execution.
| Linker | Loader |
|---|---|
| The linker is part of the library files. | The loader is part of an operating system. |
| The linker performs the linking operation. | The loader loads the program for execution. |
| It also connects user-defined functions to user-defined libraries. | Loading a program involves reading the contents of an executable file in memory. |
| Linker Combines object files into a single executable file. | Loader Loads executable files into memory for execution. |
| Object files generated by the compiler. | Executable files generated by the linker. |
| Linker is a Single executable file. | Loader loads the program into memory. |
| Linker assigns memory addresses to code and data sections. | Loader Allocates memory for the program in the process space. |
| Resolves external references between object files. | Resolves external references between executable files. |
| Linker does not execute the program. | Loader executes the program in memory. |
| Linker occurs during compilation. | Loader occurs during program execution. |
| Linking is used to join all the modules. | Loading is used to allocate the address to all executable files and this task is done by the loader. |
| Linking is performed with the help of Linker. It is also called a link editor. | A loader is a program that places programs into memory and prepares them for execution. |
Differences between static and dynamic linking¶
Static Linking (linker' task)¶
- A statically linked program takes constant load time every time it is loaded into the memory for execution.
- Static linking is performed by programs called linkers as the last step in compiling a program. Linkers are also called link editors.
- In static linking, if any of the external programs has changed then they have to be recompiled and re-linked again else the changes won’t reflect in the existing executable file.
Dynamic Linking (loader' task)¶
- Dynamic linking is performed at run time by the operating system.
- In dynamic linking, this is not the case and individual shared modules can be updated and recompiled. This is one of the greatest advantages dynamic linking offers.
- In dynamic linking load time might be reduced if the shared library code is already present in memory.
Two Types of Dynamic Linking¶
Implicit¶
- Implicit Dynamic linking is done by the loader at the loading time of the process. Loader checks import symbols (dynsym)and import libraries and loads individual shared objects accordingly. If one or more objects are already loaded then they need not to be loaded again and only shared code section will be linked to the process. It will populate import table(dynsym) and resolves all external symbols from the shared object. Once linking is done process can execute shared function directly.
Explicit¶
- Explicit Dynamic linking Another way is loading the symbol during run time explicitly. Operating system provides system calls to load a dynamic library and finding import symbol location, unloading the library etc. This way programmer can explicitly load a library and find out a symbol/function entry and execute that and then can unload that.
Relocatable Objects¶
a pure translation from the source code with .o extension suffix
some important commands¶
Linux embed assembly
Show the content of preprocessor
Export the assembly of source
Export the object of source
Print the type, arch and address of object file
Display information about ELF files
List symbols from object files
GNU linker
Trace system calls and signals
Print shared object dependencies