Memory management
ws# Memory Management
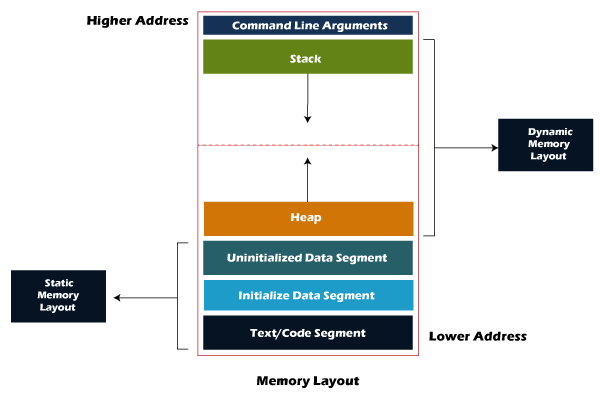
Memory Segmentation Schema¶
+------------------+
| |
⌈ | Code Segment | Binary of source code
Static | |
Memory +------------------+
Layout | |
⌊ | Data Segment | Static, Global variables & Constants
| |
+------------------+
| |
⌈ | Heap Segment | Dynamic variable size allocation
Dynamic | |
Memory +------------------+
Layout | |
⌊ | Stack Segment | Local variables & functions
| |
+------------------+
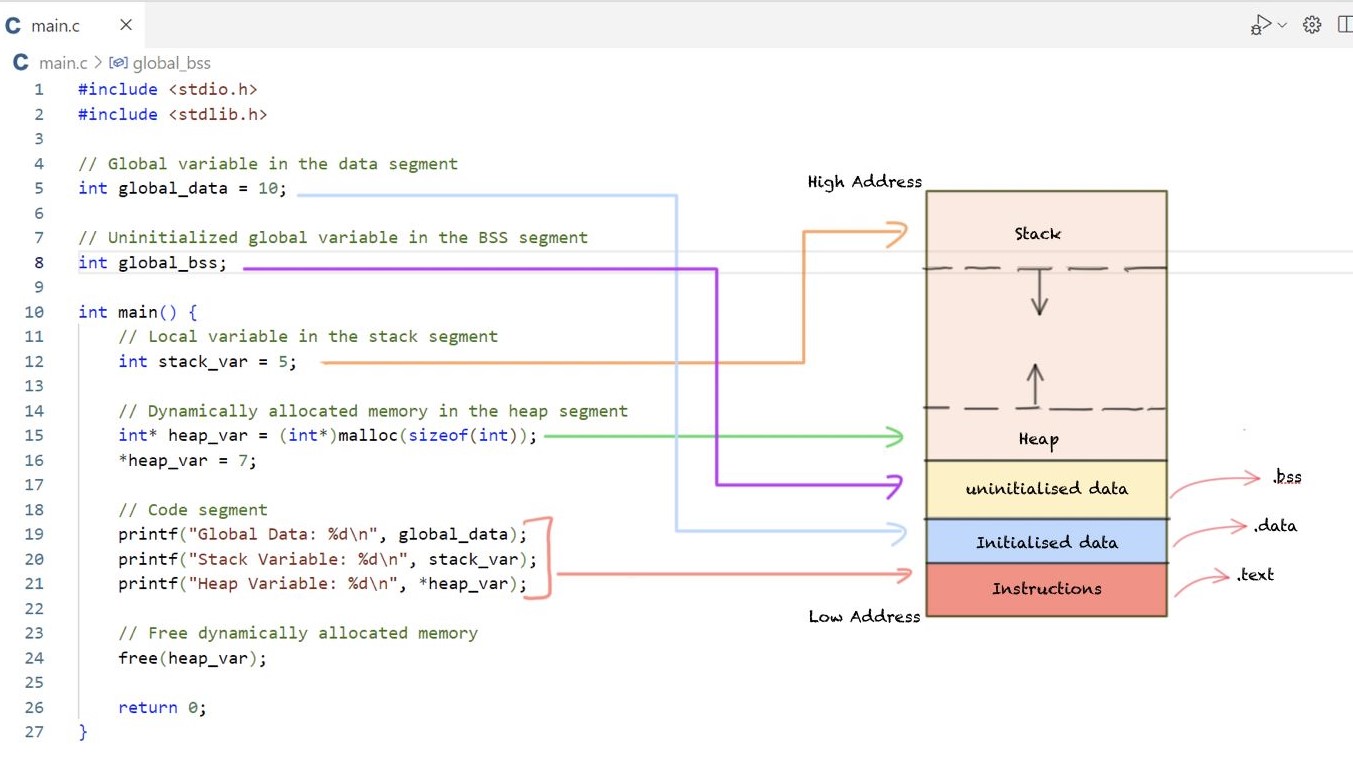
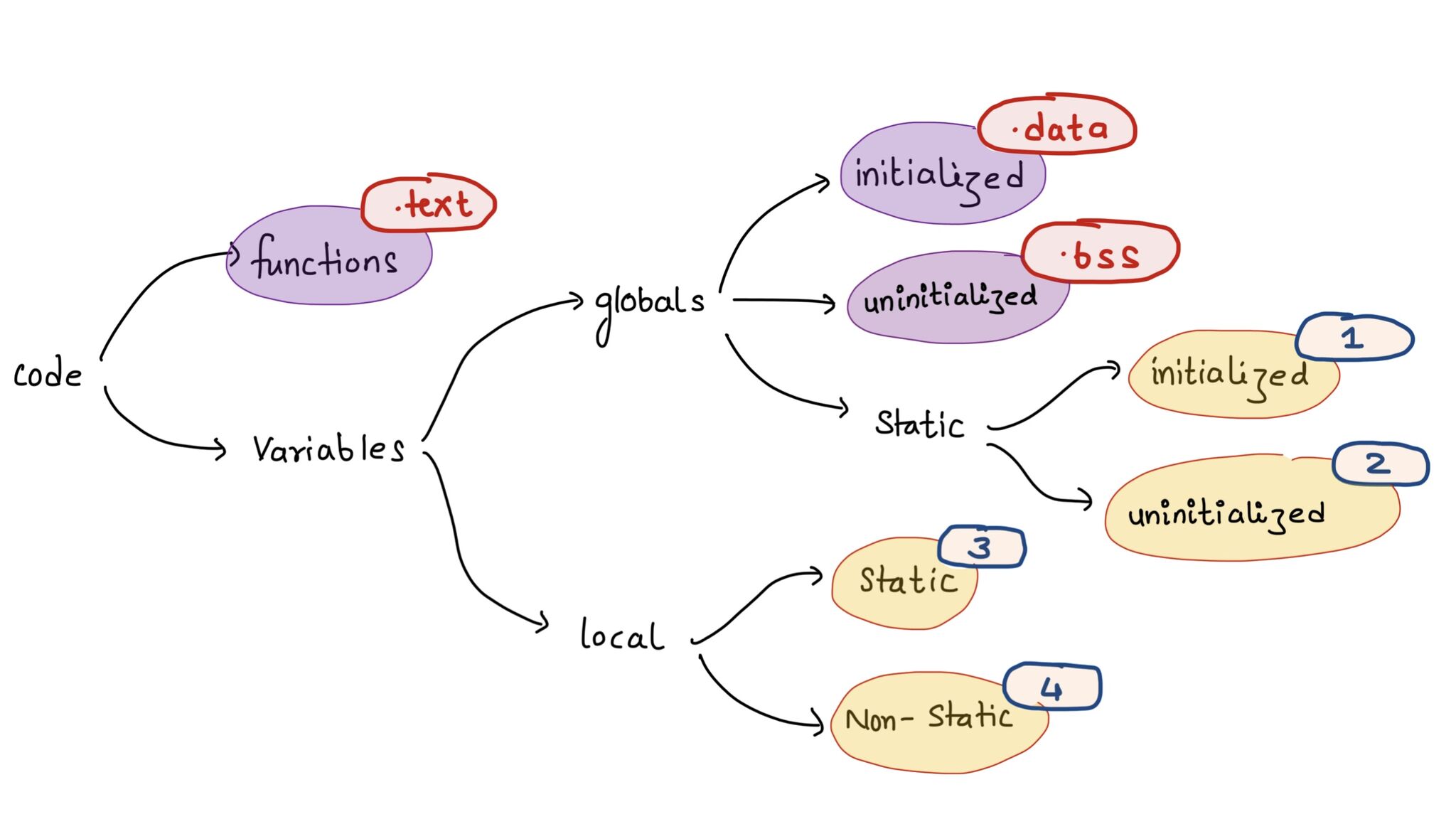
Data Segment¶
- Initialized (data)
- Uninitialized (bss)
- Read-Only Section
- Read-Write Section
+--------------------+
| Code Segment |
| |
| Instructions |
| of the Program |
| |
+--------------------+
| Data Segment |
| |
| Initialized Data | <-- .data section / Modifiable Data (R.W.)
| (static, globals, |
| e.g.) |
| Constants | <-- .rodata section (or within .data)
| |
+ - - - - - +
| |
| Uninitialized | <-- .bss section / Zeroed Data
| Data (zeroed) |
| (globals without |
| explicit values) |
| |
+--------------------+
| |
| Heap Segment |
| |
| (Dynamic Memory) |
| |
+--------------------+
| Stack Segment |
| |
| Local Variables |
| and Functions |
| |
+--------------------+
Share Memory Structure For a Thread¶
+--------------------+
| ... |
| Code ┑ |
| Data section |
| Heap ┙ |
| as same as |
| above |
| ... |
+--------------------+
| Stack (Thread 1) | Share the stack segment
| |
| Local Variables |
| and Functions |
| |
+--------------------+
| Stack (Thread 2) |
| |
| Local Variables |
| and Functions |
| |
+--------------------+
| Stack (Thread 3) |
| |
| Local Variables |
| and Functions |
| |
+--------------------+
Memory Section by Threads¶
| Memory Region | Shared | Private |
|---|---|---|
| Code Segment (Text) | Yes | No |
| Data Segment (Initialized global/static variables) BSS (Uninitialized global/static variables) |
Yes | No |
| Heap | Yes | No |
| Mapped Memory | Yes | No |
| Thread-Local Storage (TLS) | No | Yes |
| Stack | No | Yes |
| Registers (CPU) | No | Yes |
External Resources¶
- Memory Management in Operating System
- Memory Layout of C Programs
- Memory Segmentation in 8086 Microprocessor
- C Memory Division Text (code segment), Data and BSS
- Memory Management on C programming
- Memory Layout in C
How Does C Code Become Assembly¶
The compiler does a lot of stuff to translate C code to assembly
- Choose assembly instructions to implement C oeprations
- Implement C conditionals and loops using jumps and branches
- Choose registers and memory locations to store data
- Move data among the registers and memory to satifisy dependecies
- Coordinate function calls
- Try to make the assembly fast.