Getting Started with C++¶
C++:
-
C++ blends the C language with support for
object-oriented programmingandgeneric programming. -
encapsulation,data hiding,polymorphismandinheritance; these are the key concepts ofOOP. -
C++ joins three separate programming categories: the
procedural language, represented byC; theobject-oriented language, represented by theclass enhancements C++adds toC;andgeneric programming, supported byC++ templates. -
If you don’t know C, you have to master the
C components, theOOP components,and thegeneric componentsto learn C++. -
Special programs called
compilerstranslate a high-level language to the internal language of a particular computer.
C Programming Philosophy:
- computer languages deal with two concepts
dataandalgorithms. - The
dataconstitutes the information a program uses and processes. - The
algorithmsare the methods the program uses.
C Programming Philosophy:
- C is a
procedural language.That means itemphasizes the algorithm side of programming. data+algorithm=program
- With C, the idea is to
break a large program into smaller, more manageable tasks. - C’s design facilitates this approach, encouraging you to develop program units called
functionstorepresent individual task modules.
The C++ Shift Object-Oriented Programming:
- Although the principles of structured programming improved the
clarity,reliability,andease of maintenance of programs, large-scale programming still remains a challenge.OOPbrings a new approach to that challenge. - Unlike procedural programming, which emphasizes
algorithms, OOP emphasizes thedata. - The idea is to
design data forms that correspond to the essential features of a problem. - In C++,a
classis a specification describing such a new data form,and anobjectis a particular data structure constructed according to that plan. - In general,a
classdefines what data is used to represent anobjectand the operations that can be performed on that data. -
The process of going from a
lower levelof organization, such asclasses, to ahigher level, such asprogram design, is calledbottom-upprogramming. -
OOP facilitates:
-
Information hiding(encapsulation) safeguards data from improper access Polymorphismlets you create multiple definitions foroperatorsandfunctions,with the programming context determining which definition is used.-
Inheritancelets you derive new classes from old ones. -
C++ and Generic Programming:
-
whereas OOP emphasizes the
data aspect of programming, generic programming emphasizesindependence from a particular data type. -
OOPis a tool formanaging large projects, whereasgeneric programmingprovides tools forperforming common tasks, such as sorting data or merging lists. -
The term generic refers to code that is
type independent. -
Portability and Standards:
-
If you can
recompilethe programwithout making changesand it runs without a hitch, we say the program isportable. -
Linking combines
your object codewithobject code for the functions you useand withsome standard startup codeto pro-duce a runtime version of your program.The file containing this final product is called the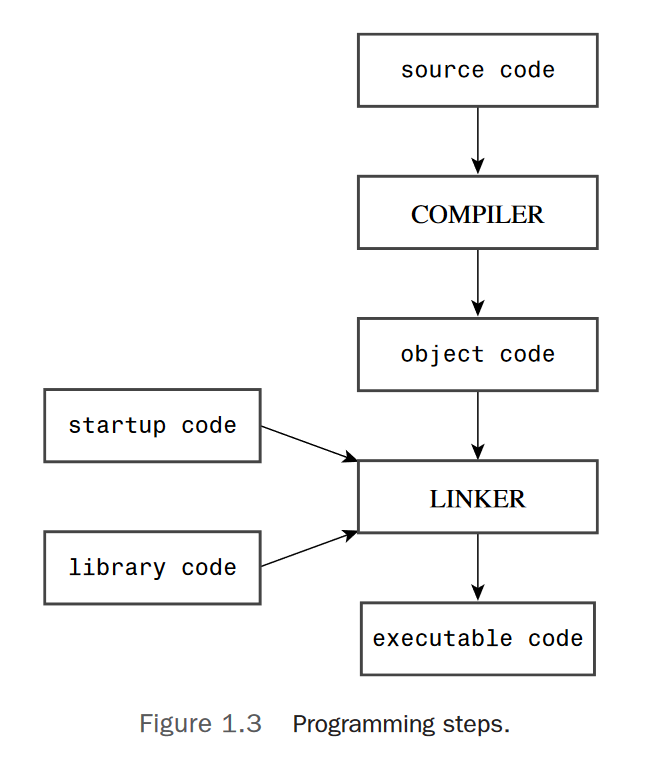
-
Compilation and Linking:
-
Originally, Stroustrup implemented C++ with a
C++-to-C compilerprogram instead of developing a directC++-to-objectcode compiler.This program, calledcfront(for C front end), translated C++ source code to C source code, which could then be compiled by a standard C compile. -
As C++ has developed and grown in popularity, more and more implementers have turned to creating C++ compilers that generate
object code directly from C++ source code. -
Linux Compiling and Linking:
- Linux systems most commonly use g++, the
GNU C++ compilerfrom the Free Software Foundation.- g++ spiffy.cxx
- Some versions might require that you link in the C++ library:
- g++ spiffy.cxx -lg++
- To compile multiple source files, you just list them all in the command line:
- g++ my.cxx precious.cxx
- compile with custom object file name:
- g++ my.cxx precious.o